|
NEUROVASCULAR COMPRESSION |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
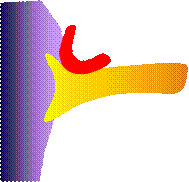
Microvascular
decompression as an surgical method aims to remove a so-called neurovascular
compression. Under micro-surgical conditions, the affected cranial nerve is
demonstrated in the posterior cranial fossa and the contact between the
vascular loop and the root entry zone of the cranial nerve at the brain stem
is identified. The blood vessel is then carefully removed from the nerve and
slightly displaced, as not to interrupt the blood supply. In order to prevent
the vessel from falling back into its former position, the contact area is
padded with Teflon. Access to the nerves in the posterior cranial fossa is
performed through a small (approx. 2-3 cm) opening in the skull behind the
ear.
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
Principle of
microvascular decompression |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
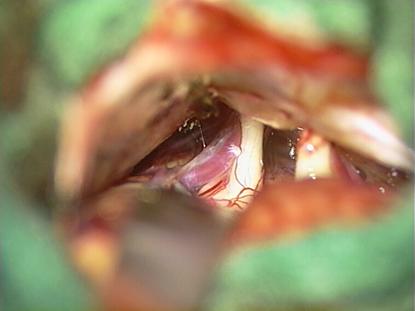
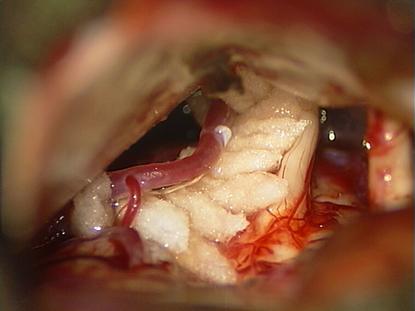
Microsurgical
view into the posterior fossa dor microvascular decompression. Identification
of the trigeminal nerve and a vessel compressibg the nerve close to the
brainstem. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
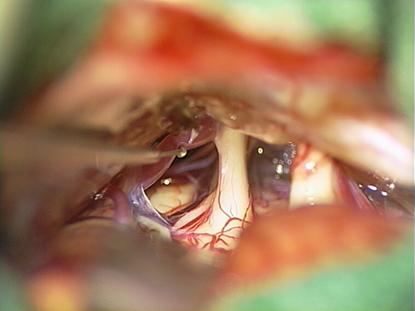
Clear contact
between the trigeminal nerve and the vessel (A. cerebelli superior). |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
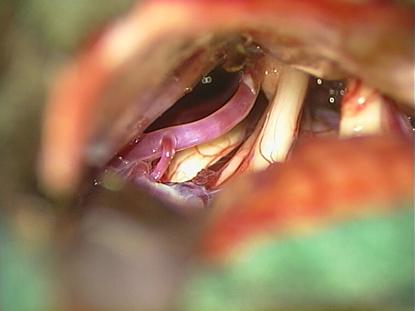
After
dissection of the arachnoid
neurovascular compression on the nerven it clearly visible. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
Mobilisation
of the vascular loop from the nerve. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
Positioning of
Teflon |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
Complete mikrovascular
decompression of the nerve. A new contacting is impossible now. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
NVCHOME.COM |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
R. NARAGHI |
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|